More Hydrogen Less Methane about the Same HO
July 24, 2022Recently a bunch of wanna be paid attentiontos have made a grab for the majic ring by selling their view that the global warming effect of hydrogen is gonna be major. As usual such rumors spread like lightning on Twitter and the like.
Uncle Eli is here to tell you that this is finger on the scale stuff. The kick off was "Global modelling studies of hydrogen and its isotopomers using STOCHEM-CRI: Likely radiative forcing consequences of a future hydrogen economy", Richard G. Derwent, David S. Stevenson, Steven R. Utembe, Michael E. Jenkin, Anwar H. Khan, Dudley E. Shallcross International Journal of Hydrogen Energy Volume 45, 18 March 2020, Pages 9211-922
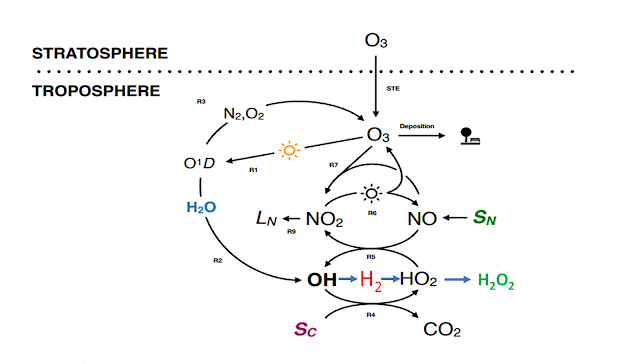
It goes like this, Derwent, et al. modelled the effect of injecting a pulse of 1.67 Tg of H2 into the atmosphere and find that it has a global warming potential of 5 on a 100 year basis. Their model shows that this is because the H2 reacts with HO radicals which are thus not available to react with methane, CH4, so the concentration of methane, an important greenhouse gas will be higher. There is also a secondary effect where ozone, O3, is produced.
The TL:DR or as the bunnies call it today, a Tweet, is that
The simplified kinetics of HO in the atmosphere is an equilibrium between HO and HO2. HO is very reactive and once formed finds something, anything that is not totally oxidized like CO2, to react with. It only lasts for a second or so. HO2 is much less reactive, but still lasts for maybe ten times as long. There is a constant interchange between them and regeneration by other reactions.H2 is introduced to take the place of CH4 so to make an honest calculation of what happens in a hydrogen economy, (finger off the scale) you not only have to pulse H2 emissions but also decrease CH4 emissions by a similar amount.
Sc is the reaction of HO with CO, which accounts for 40-50% of HO reactions in the atmosphere, methane accounts for about 15%, the rest being ozone and other hydrocarbons but on a rough basis Sc is the reaction of HO with any carbon containing molecule except the totally oxidized CO2 .